essentially yes. you will can only observe the equilibrium price, and the curves are an abstraction of all the possible interactions of producers and consumers in a competitive market. there are ways of deducing these curves, but they are kinda tautological. also like, the curves were made curves only because it looked like newton’s graphs, which makes them more scientific by association (pic from Doughnut Economics by Kate Raworth).
My question would be, why do we want to model supply and demand in the first place? As we see in liberal economics, supply and demand is just used as a justification for pushing deregulation policies. if you want to use the model for other means, the problem is that it’s only useful in markets of perfect competition, which are very rare. perfect competition occurs where there are virtually infinite producers (because the barrier to entry is super low) and the products are identical. i like the example of apples or potatoes in a farmers market. producers have to set the ‘market price’ because otherwise people will buy the other thing that’s the same and cheaper (but then you assume that people don’t have a favourite stall, all the producers haven’t colluded etc etc). most of the time you have a monopoly or oligopoly situation, so supply and demand equilibrium becomes meaningless, because the firms can set any prices they want.
for recommendations, i like unlearning economics I like his debunking of liberal econ (disclaimer that i disagree with his views on market socialism and LTV). check out the ‘death of econ 101’ video for supply and demand stuff. Doughnut Economics which i mentioned is a pretty good debunking of models that advocate for growth and free markets, it’s a light read. it is more focused on sustainability rather than socialism, but i think it’s good at suggesting alternative ways at looking at an economy. for instance as a cycle rather than an intersection of lines (Marx did it first but whatever, i like cool graphs). i would also recommend looking into the field of behavioral economics, since it’s whole purpose is to debunk the liberal claim that people in a market are ‘rational actors’.
i also recommend this course on economics4emancipations website for a brief socialist oriented economics course (not really about debunking though). it has really good readings suggestions as well.
i guess my main point would be just to keep in mind when looking at a model: what does this assume about humans and relations? what is the goal of the person presenting the model? is this model backed up with statistically significant evidence?
sorry for the a bit long reply, it’s my area so i have quite some thoughts on it. would love to answer any more specific questions anytime too
essentially yes. you will can only observe the equilibrium price, and the curves are an abstraction of all the possible interactions of producers and consumers in a competitive market. there are ways of deducing these curves, but they are kinda tautological. also like, the curves were made curves only because it looked like newton’s graphs, which makes them more scientific by association (pic from Doughnut Economics by Kate Raworth).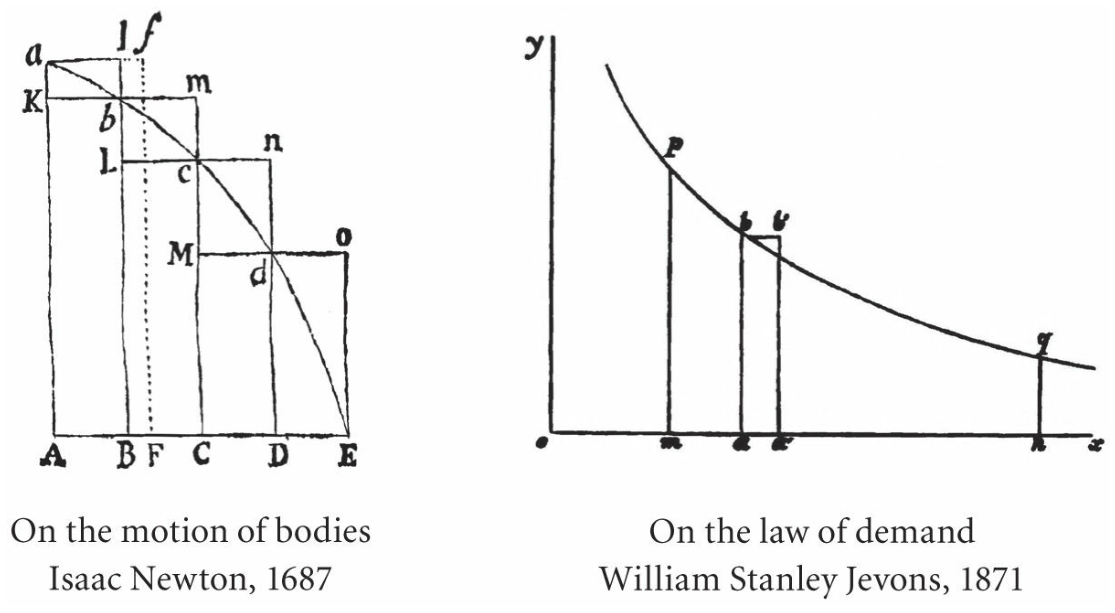
Is there a better model of supply and demand? And what is a good debunking of bourgeois economics? Can you recommend books or videos or articles?
My question would be, why do we want to model supply and demand in the first place? As we see in liberal economics, supply and demand is just used as a justification for pushing deregulation policies. if you want to use the model for other means, the problem is that it’s only useful in markets of perfect competition, which are very rare. perfect competition occurs where there are virtually infinite producers (because the barrier to entry is super low) and the products are identical. i like the example of apples or potatoes in a farmers market. producers have to set the ‘market price’ because otherwise people will buy the other thing that’s the same and cheaper (but then you assume that people don’t have a favourite stall, all the producers haven’t colluded etc etc). most of the time you have a monopoly or oligopoly situation, so supply and demand equilibrium becomes meaningless, because the firms can set any prices they want.
for recommendations, i like unlearning economics I like his debunking of liberal econ (disclaimer that i disagree with his views on market socialism and LTV). check out the ‘death of econ 101’ video for supply and demand stuff. Doughnut Economics which i mentioned is a pretty good debunking of models that advocate for growth and free markets, it’s a light read. it is more focused on sustainability rather than socialism, but i think it’s good at suggesting alternative ways at looking at an economy. for instance as a cycle rather than an intersection of lines (Marx did it first but whatever, i like cool graphs). i would also recommend looking into the field of behavioral economics, since it’s whole purpose is to debunk the liberal claim that people in a market are ‘rational actors’.
i also recommend this course on economics4emancipations website for a brief socialist oriented economics course (not really about debunking though). it has really good readings suggestions as well.
i guess my main point would be just to keep in mind when looking at a model: what does this assume about humans and relations? what is the goal of the person presenting the model? is this model backed up with statistically significant evidence?
sorry for the a bit long reply, it’s my area so i have quite some thoughts on it. would love to answer any more specific questions anytime too