- cross-posted to:
- news@hexbear.net
- cross-posted to:
- news@hexbear.net
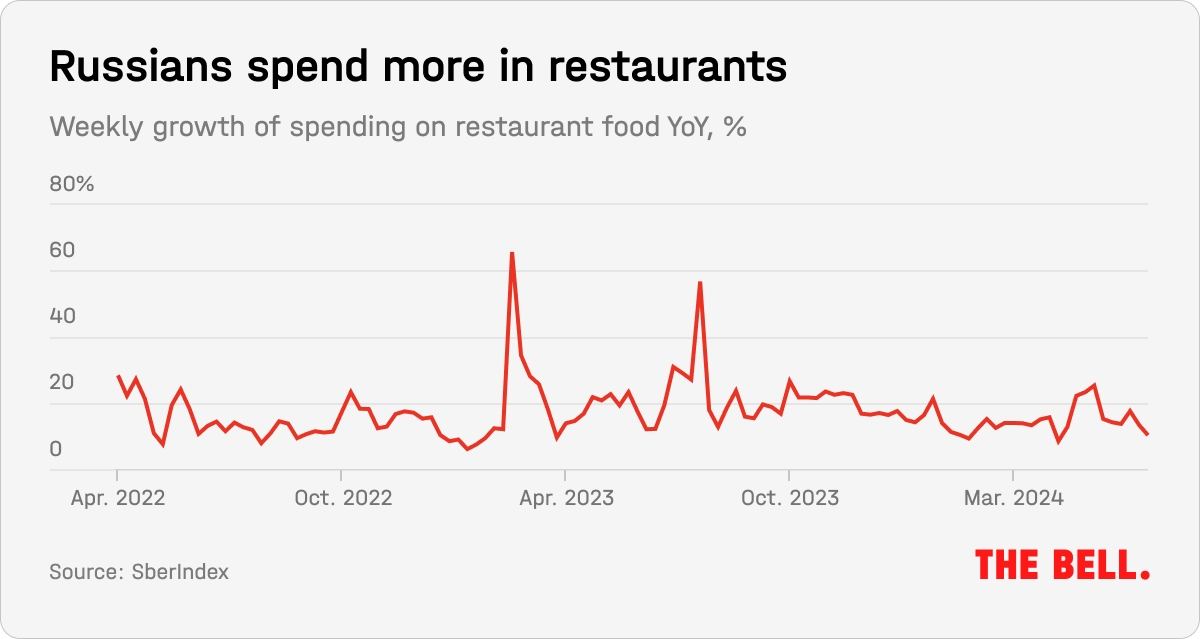
Most Russians have never lived as well as they do now. Nor do people believe that things are about to get worse. The fact that Russians are living better is evident from their outgoings. Spending at cafes and restaurants, for example, is increasing.
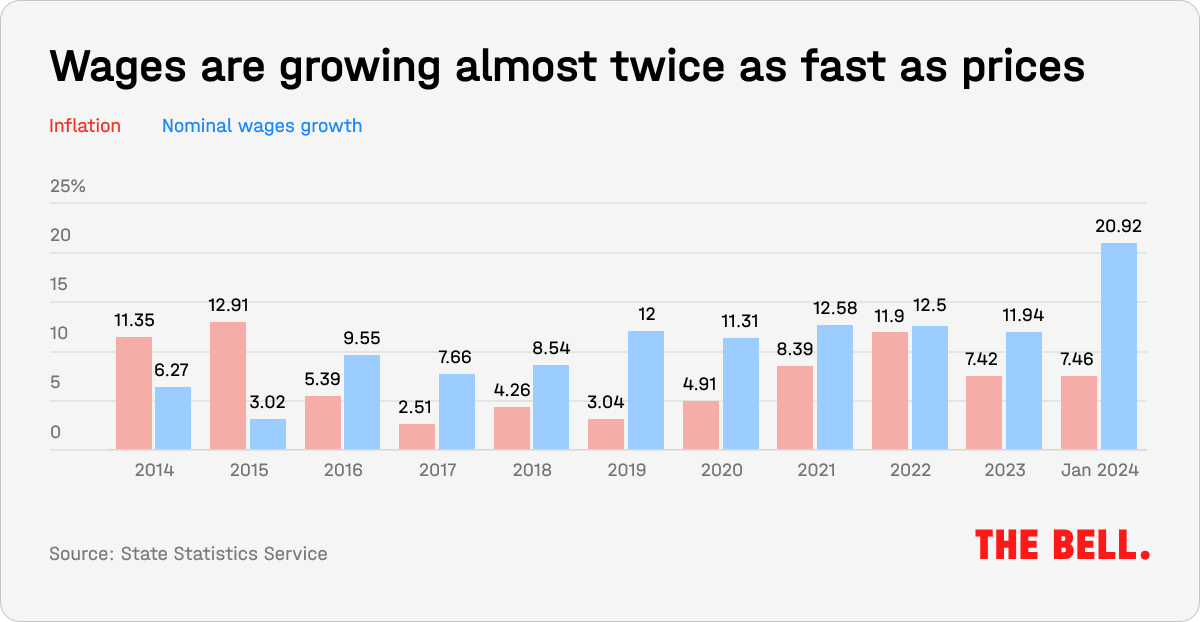
After the start of the war, inflation rocketed – but wages more than kept pace.
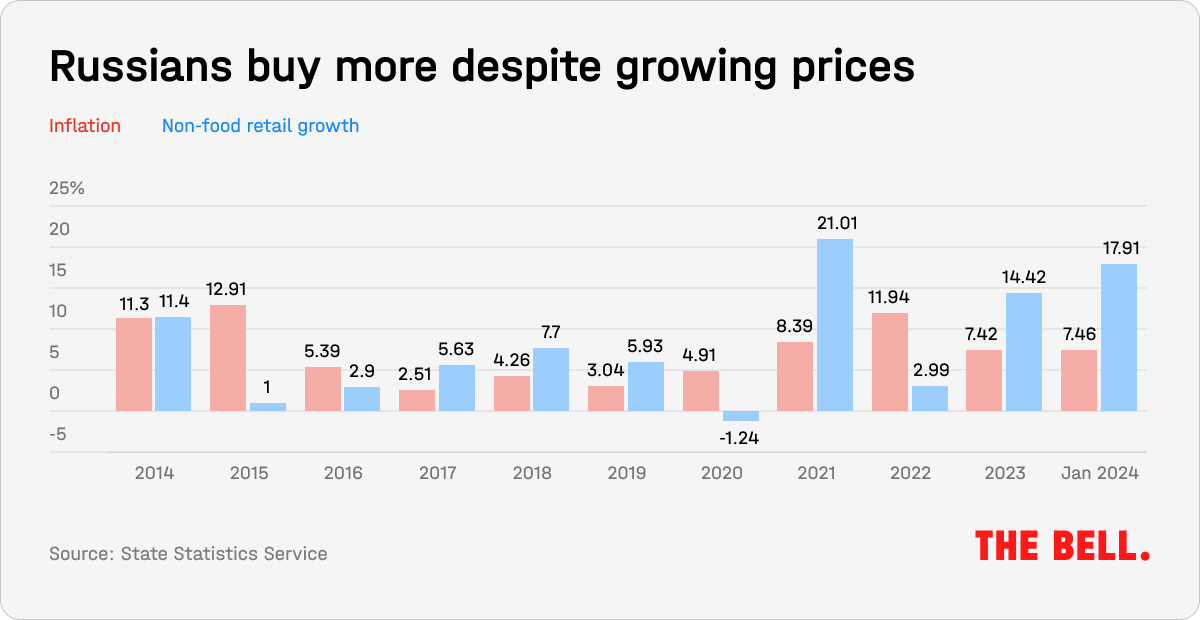
Demand for non-food goods (i.e. items where purchases can be postponed or even canceled) has recovered from its slump in the months after the full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Its rate of growth now exceeds both inflation, and wage increases.
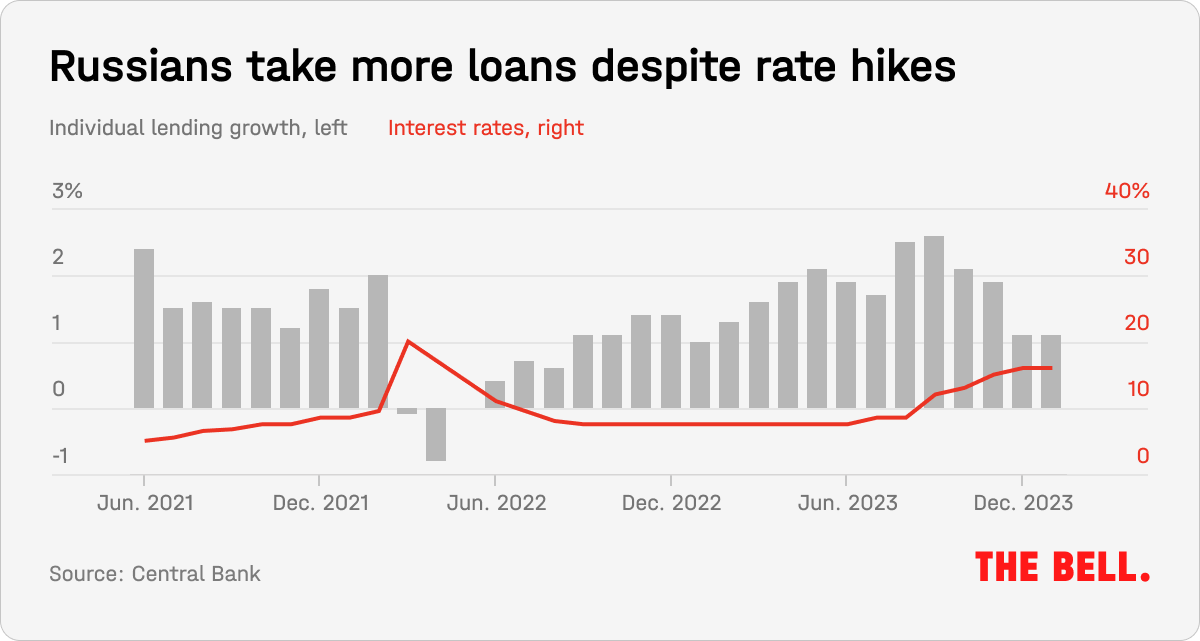
This does not look like the sort of panic buying that happens in a crisis, when many rush out to buy whatever consumer durables they can afford. Instead, Russians appear to have sufficient confidence in their finances to take out personal loans. Consumer confidence is approaching record levels, Nabiullina told reporters on Friday.
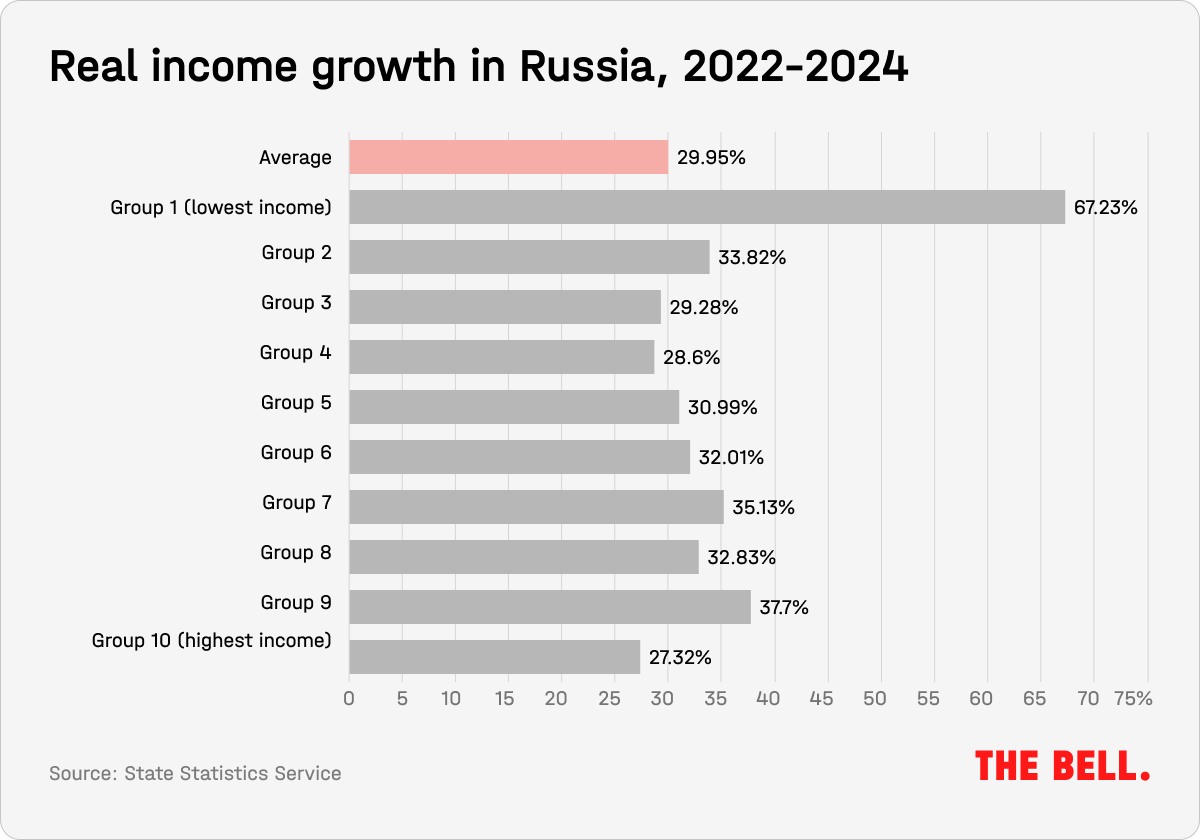
Of course, increased prosperity is not universal. But those who have lost out are the more wealthy Russians. The average income of the richest 10% in Russian society has increased by 27% since the start of the war. While this may seem a lot, it’s the lowest rise of all 10 income groups, and barely matches the combined inflation rate for the past two years. Incomes for the poorest in society have grown much faster.



On background note, the GDP and the flawed financial measurement criteria by the Bretton Woods institutions do not measure cost of living because it will disprove the belief that Capitalism, which is a economic system that concentrates wealth to a few landowners contrary to the de jure Pax Americana redefinition, eliminates poverty. The Pax Americana creates the assumption that all countries and regions have minimal living expense requirement of $2 USD, and then use the high short-term financial growth under Capitalism to prove that Capitalism is eliminating poverty even when the temporary high financial growth masks decline in other dimensions that will lead to long-term financial regression.