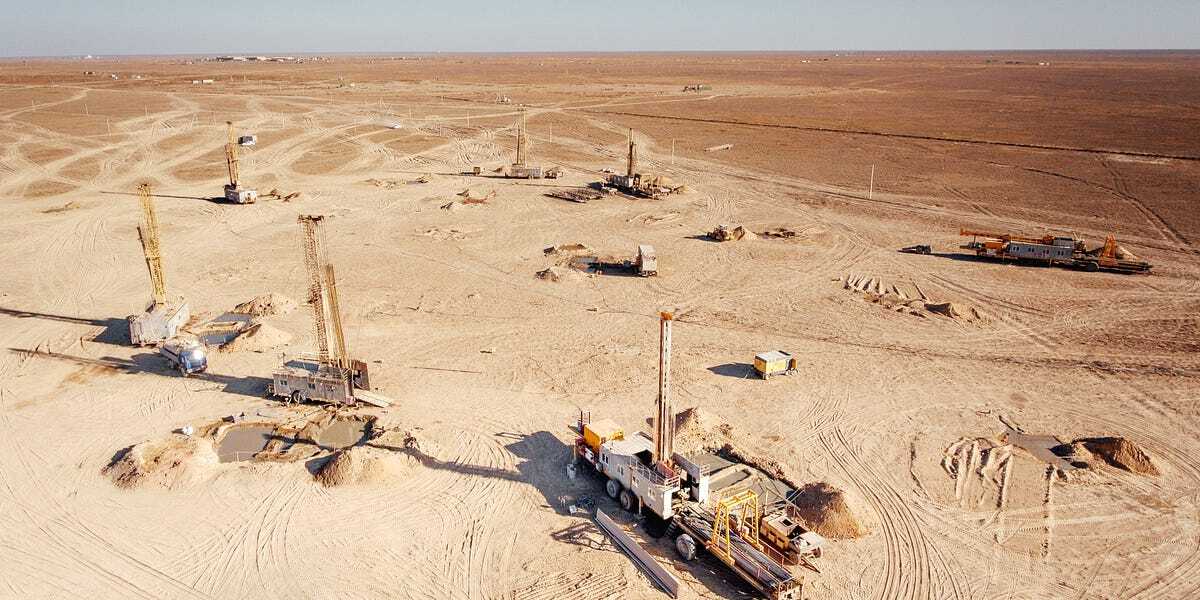
I found this article to be interesting as it talks a bit about methods of mining uranium, as well as talks about a current issue regarding a shortage of a necessary ingredient of that process (sulfuric acid), while also going over issues in how to transport uranium supply to the West in light of sanctions on transport routes through Russia and recent deals with China. In general the article is just stressing how precarious the West’s supply of uranium from Central Asia may be, and highlighting that China and Russia are much better positioned to trade with that region. Also a mention of how France has been prompted to rely more on Central Asia for uranium in light of the instability of sourcing uranium from Niger.
- Kazatomprom, world’s largest uranium producer, warns of production shortfall
- logistical issues, eg transport and shortages in sulfuric acid could take years to fix
- concerns long-term supply contracts prioritize Russia and China over the West
Kazatomprom is the world’s largest and, arguably, most important uranium producer, accounting for 23% of global supply in 2022. To put in context, that’s double the next largest producer, Cameco in Canada.
The company has now warned production will be 20% below levels allowed by permits in 2024, with production impacted possibly into 2025. The warning comes just as uranium prices are approaching historic highs with significant fallout across the global energy and nuclear sector.
Critically, as we’ll get to shortly, Kazatomprom mines exclusively with in-situ leach (ISL) methods (or, in-situ recovery (ISR)), which involves dissolving the ore while it’s still in the ground with acid and soda, and then pumping the solution to the ground where it can be recovered with no tailings, waste or disturbance on the surface. […] The main problem, ostensibly, is that they don’t have enough sulfuric acid, essential for in-situ leaching, to raise output levels. […] The problem is so acute that Kazatomprom plans to construct a new sulfuric acid plant in the Turkestan region to produce 800,000 tonnes of sulfuric acid per year. However, it’s only expected to be ready in 2026.
The deals between Kazatomprom and both Russia and China threaten to squeeze out Western access. […] China has just signed a long-term contract to procure a significant amount of uranium — for domestic consumption, not for export. The West, we suspect, would also be reluctant to trade vulnerable supply chains through Russia for supply chains through China. […] In the high-stakes Great Game of resource control in Central Asia, any sudden and severe tightening of global uranium supply threatens to expose the West’s precarious position compared to its competitors.