The wolf (Canis lupus;[b] pl.: wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gray wolves, as popularly understood, only comprise naturally-occurring wild subspecies. The wolf is the largest extant member of the family Canidae, and is further distinguished from other Canis species by its less pointed ears and muzzle, as well as a shorter torso and a longer tail. The wolf is nonetheless related closely enough to smaller Canis species, such as the coyote and the golden jackal, to produce fertile hybrids with them. The wolf’s fur is usually mottled white, brown, gray, and black, although subspecies in the arctic region may be nearly all white.
Of all members of the genus Canis, the wolf is most specialized for cooperative game hunting as demonstrated by its physical adaptations to tackling large prey, its more social nature, and its highly advanced expressive behaviour, including individual or group howling. It travels in nuclear families consisting of a mated pair accompanied by their offspring. Offspring may leave to form their own packs on the onset of sexual maturity and in response to competition for food within the pack. Wolves are also territorial, and fights over territory are among the principal causes of mortality. The wolf is mainly a carnivore and feeds on large wild hooved mammals as well as smaller animals, livestock, carrion, and garbage. Single wolves or mated pairs typically have higher success rates in hunting than do large packs. Pathogens and parasites, notably the rabies virus, may infect wolves.
The global wild wolf population was estimated to be 300,000 in 2003 and is considered to be of Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Wolves have a long history of interactions with humans, having been despised and hunted in most pastoral communities because of their attacks on livestock, while conversely being respected in some agrarian and hunter-gatherer societies. Although the fear of wolves exists in many human societies, the majority of recorded attacks on people have been attributed to animals suffering from rabies. Wolf attacks on humans are rare because wolves are relatively few, live away from people, and have developed a fear of humans because of their experiences with hunters, farmers, ranchers, and shepherds.
Etymology
The English “wolf” stems from the Old English wulf, which is itself thought to be derived from the Proto-Germanic *wulfaz. The Proto-Indo-European root *wĺ̥kʷos may also be the source of the Latin word for the animal lupus (*lúkʷos).
Evolution
The earliest fossils of C. lupus were found in what was once eastern Beringia at Old Crow, Yukon, Canada, and at Cripple Creek Sump, Fairbanks, Alaska. The age is not agreed upon but could date to one million years ago. Considerable morphological diversity existed among wolves by the Late Pleistocene. They had more robust skulls and teeth than modern wolves, often with a shortened snout, a pronounced development of the temporalis muscle, and robust premolars. It is proposed that these features were specialized adaptations for the processing of carcass and bone associated with the hunting and scavenging of Pleistocene megafauna. Compared with modern wolves, some Pleistocene wolves showed an increase in tooth breakage similar to that seen in the extinct dire wolf. This suggests they either often processed carcasses, or that they competed with other carnivores and needed to consume their prey quickly. Compared with those found in the modern spotted hyena, the frequency and location of tooth fractures in these wolves indicates they were habitual bone crackers.
Description
The wolf is the largest extant member of the Canidae family, and is further distinguished from coyotes and jackals by a broader snout, shorter ears, a shorter torso and a longer tail. It is slender and powerfully built, with a large, deeply descending rib cage, a sloping back, and a heavily muscled neck. The wolf’s legs are moderately longer than those of other canids, which enables the animal to move swiftly, and to overcome the deep snow that covers most of its geographical range in winter. The ears are relatively small and triangular. The wolf’s head is large and heavy, with a wide forehead, strong jaws and a long, blunt muzzle.
The wolf has very dense and fluffy winter fur, with a short undercoat and long, coarse guard hairs. Most of the undercoat and some guard hairs are shed in spring and grow back in autumn. The longest hairs occur on the back, particularly on the front quarters and neck. Especially long hairs grow on the shoulders and almost form a crest on the upper part of the neck.
A wolf’s coat colour is determined by its guard hairs. Wolves usually have some hairs that are white, brown, gray and black.
Distribution and habitat
Wolves occur across Eurasia and North America. However, deliberate human persecution because of livestock predation and fear of attacks on humans has reduced the wolf’s range to about one-third of its historic range; the wolf is now extirpated (locally extinct) from much of its range in Western Europe, the United States and Mexico, and completely in the British Isles and Japan. In modern times, the wolf occurs mostly in wilderness and remote areas. The wolf can be found between sea level and 3,000 m (9,800 ft). Wolves live in forests, inland wetlands, shrublands, grasslands (including Arctic tundra), pastures, deserts, and rocky peaks on mountains. Habitat use by wolves depends on the abundance of prey, snow conditions, livestock densities, road densities, human presence and topography.
Diet
Like all land mammals that are pack hunters, the wolf feeds predominantly on ungulates that can be divided into large size 240–650 kg (530–1,430 lb) and medium size 23–130 kg (51–287 lb), and have a body mass similar to that of the combined mass of the pack members. The wolf specializes in preying on the vulnerable individuals of large prey, with a pack of 15 able to bring down an adult moose. The variation in diet between wolves living on different continents is based on the variety of hoofed mammals and of available smaller and domesticated prey
Nonetheless, wolves are not fussy eaters. Smaller-sized animals that may supplement their diet include rodents, hares, insectivores and smaller carnivores. They frequently eat waterfowl and their eggs. When such foods are insufficient, they prey on lizards, snakes, frogs, and large insects when available. Wolves in some areas may consume fish and even marine life. Wolves also consume some plant material.
Interactions with other predators
Wolves typically dominate other canid species in areas where they both occur. In North America, incidents of wolves killing coyotes are common, particularly in winter, when coyotes feed on wolf kills. Wolves may attack coyote den sites, digging out and killing their pups, though rarely eating them. There are no records of coyotes killing wolves, though coyotes may chase wolves if they outnumber them.
Brown bears typically dominate wolf packs in disputes over carcasses, while wolf packs mostly prevail against bears when defending their den sites. Both species kill each other’s young.
Wolves encounter cougars along portions of the Rocky Mountains and adjacent mountain ranges. Wolves and cougars typically avoid encountering each other by hunting at different elevations for different prey (niche partitioning). This is more difficult during winter.
Wolf and Siberian tiger interactions are well-documented in the Russian Far East, where tigers significantly depress wolf numbers, sometimes to the point of localized extinction.
Status and conservation
The global wild wolf population in 2003 was estimated at 300,000. Wolf population declines have been arrested since the 1970s. This has fostered recolonization and reintroduction in parts of its former range as a result of legal protection, changes in land use, and rural human population shifts to cities. Competition with humans for livestock and game species, concerns over the danger posed by wolves to people, and habitat fragmentation pose a continued threat to the wolf. Despite these threats, the IUCN classifies the wolf as Least Concern on its Red List due to its relatively widespread range and stable population. The species is listed under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), meaning international trade in the species (including parts and derivatives) is regulated. However, populations of Bhutan, India, Nepal and Pakistan are listed in Appendix I which prohibits commercial international trade in wild-sourced specimens.
Megathreads and spaces to hang out:
- 📀 Come listen to music and Watch movies with your fellow Hexbears nerd, in Cy.tube
- 💖 Come talk in the New Weekly Queer thread
- 🔥 Read and talk about a current topics in the News Megathread
- ⚔ Come talk in the New Weekly PoC thread
- ✨ Talk with fellow Trans comrades in the New Weekly Trans thread
reminders:
- 💚 You nerds can join specific comms to see posts about all sorts of topics
- 💙 Hexbear’s algorithm prioritizes comments over upbears
- 💜 Sorting by new you nerd
- 🌈 If you ever want to make your own megathread, you can reserve a spot here nerd
- 🐶 Join the unofficial Hexbear-adjacent Mastodon instance toots.matapacos.dog
Links To Resources (Aid and Theory):
Aid:
Theory:
I am now 28.
ok boomer
Happy birthday!


I wish I would have been based when I was 28
probably one of the youngest here
Real? I ain’t 28 yet lol, does hexbear skew older?
Honestly I dont know. The communist I know are usually older than 25. Yeah but thats just a anecdote.
Uncritical support to 25+ comrades

90% of this site still can’t legally drink.
welcome to being 28


Communists be like: the middle class isn’t real
Then explain to me why almost everyone I meet who make more than like 50k a year act like a complete troglodyte???
More like the mid class
it’s because those higher wages kinda act like bribes
STOP acknowledging the passage of time! NOW!


2024 was three billion years ago, feel old yet?
More time has passed between now and the last airing of a Star Trek TNG episode, than there was between the airing of the last TOS episode and the airing of the last TNG episode.
This mega doesn’t have enough pictures of wolves. I hope there’s someone that can add some more.
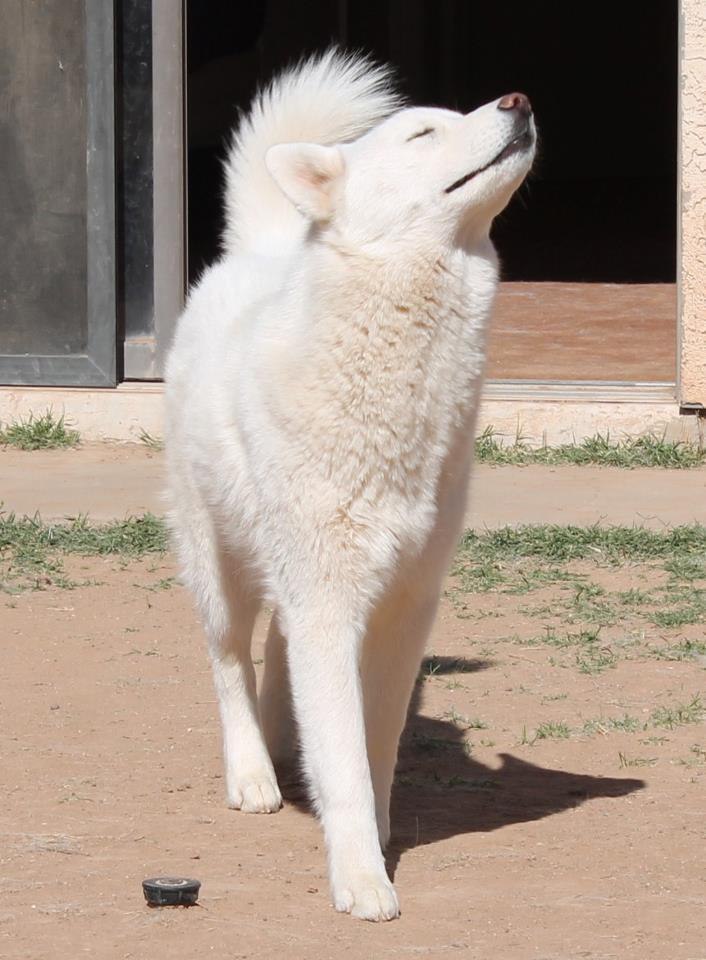

Ah! I needn’t worry


happy easter!
more like gay wolf lmao
More like removed wolf!
so true!
So mature.


congrats on getting your own mega

Feilx has gotten into Lesbian lore
Can’t wait for next chapo episode now

My buddy got confronted today for having a “gringa fetish.” He’s considered one of the most attractive men in the area and he’s always been romantically involved with pale foreign women from the US or Europe.
Local women became agitated and actually confronted him in person about it lol
I fundamentally do not view US society, government, or economy as legitimate or justifiable, and that makes my takes almost incomprehensible to people who do.
Went on the rats subreddit and they are cute little dudes but idk if I could handle getting attached to a pet knowing it’ll die in 4 years max
as the resident hamster expert, i can confirm that it is exactly as hard as you think it is
doesn’t mean it isn’t worth it though


Same. I had a bunch of rescue potatoes over the course of 3-4 years and i had to stop, it was just too hard. They’re such wonderful little fuzzballs, it’s not fair they live such short lives.
damn i’m hot. i just got 6 followers on twitter who are all attractive women in beachwear who all follow ~4,500 people each and never post anything. they seemed to love my twitter account where i also never post anything. they can just tell how hot i am